Zirconium Alloys 101

Zirconium Alloys 101
Zirconium is a silvery-white transition metal with a very low thermal neutron absorption cross-section, high hardness, good ductility, and corrosion resistance. Zirconium alloy is a solid solution of zirconium or other metals. The main use of zirconium alloys is in the field of nuclear technology, such as fuel rods in nuclear reactors. Beyond the basics above, what else should we know about zirconium alloys? In this article, we will take a close look at zirconium alloys.
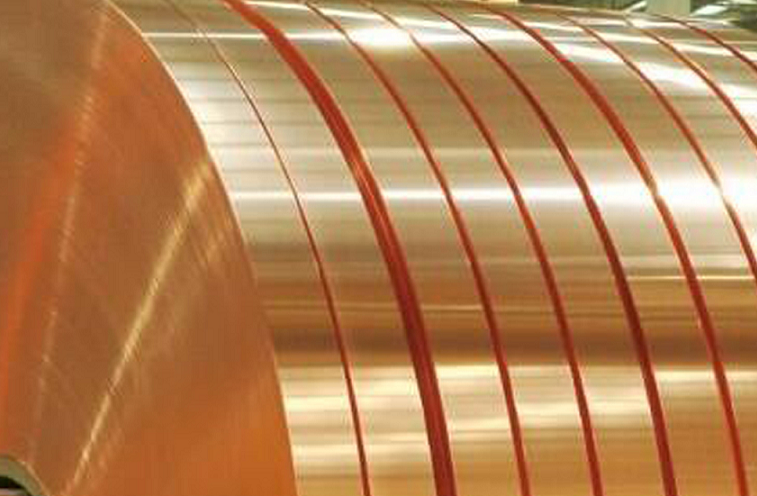

Zirconium Alloys
1. Development of Zirconium Alloy
In the late 1940s, in order to explore the applications of zirconium in water-cooled reactors, the United States began to study zirconium-based alloys.
By the mid-1950s, the United States developed the Zrca-loy-2 alloy with excellent comprehensive properties and used it as the nuclear fuel cladding material for the world's first nuclear submarine. Later, the United States successfully developed Zr-4Nb, Zr-1Nb, and Zr-2.5Nb alloys.
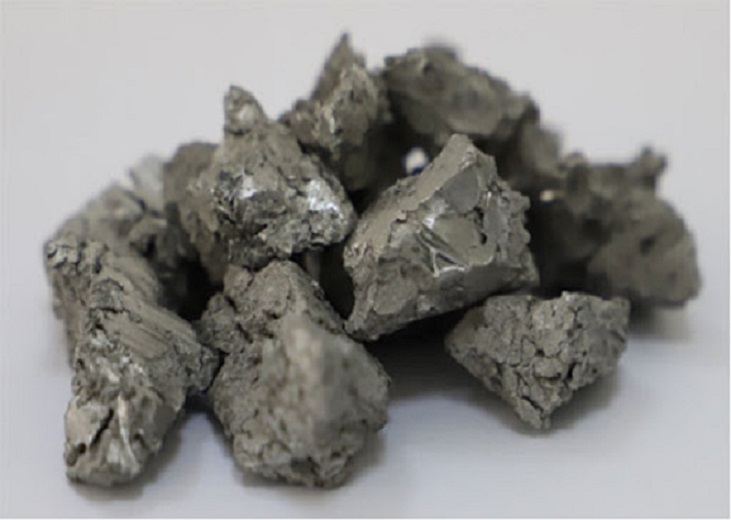

Sponge Zirconium
From sponge zirconium to zirconium alloy, countries that have achieved industrial production include the United States, Russia, France, Germany, Canada, and China.
2. Types of Zirconium Alloys
There are two series of zirconium-based alloys produced on an industrial scale: the zirconium-tin series and the zirconium-niobium series. The representative of the former is Zr-2 alloy, and the latter is Zr-2.5Nb alloy.
In the zirconium-tin series alloy, the addition of tin, iron, chromium, and nickel can improve the strength and corrosion resistance of the material, the thermal conductivity of the corrosion-resistant film, and reduce the sensitivity of the surface state to corrosion.
In the zirconium-niobium series alloys, when the additional amount of niobium reaches the solid solution limit of α-Zr at the use temperature, the corrosion resistance of the alloy is the best.
3. Welding of Zirconium and Zirconium Alloy
Zirconium and zirconium alloys have good fusion welding performance and commonly used welding methods include tungsten arc welding and electron beam welding. However, zirconium dust is flammable, so one must pay attention to safety when grinding and cutting zirconium products.
4. Properties and Applications of Zirconium Alloy
Zirconium alloy has good corrosion resistance in high-temperature and high-pressure water and steam at 300 ~ 400 ℃. In addition, zirconium alloy has moderate mechanical properties, low atomic thermal neutron absorption cross-section, and good compatibility with nuclear fuel, so it can be used as the core structure material of water-cooled nuclear reactors, which is the main purpose of zirconium alloy.
Besides, zirconium has excellent corrosion resistance to various acids (such as hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, sulfuric acid, and acetic acid), alkalis, and salts, so zirconium alloys are also used to make corrosion-resistant parts.
In addition, zirconium has a strong affinity with oxygen, nitrogen, and other gases, so zirconium and zirconium alloys are also widely used as non-evaporable getters in the electric vacuum and bulb industries. At the same time, zirconium also has excellent light-emitting properties, so it becomes a flash and firework material.
Applications of Zirconium Alloys
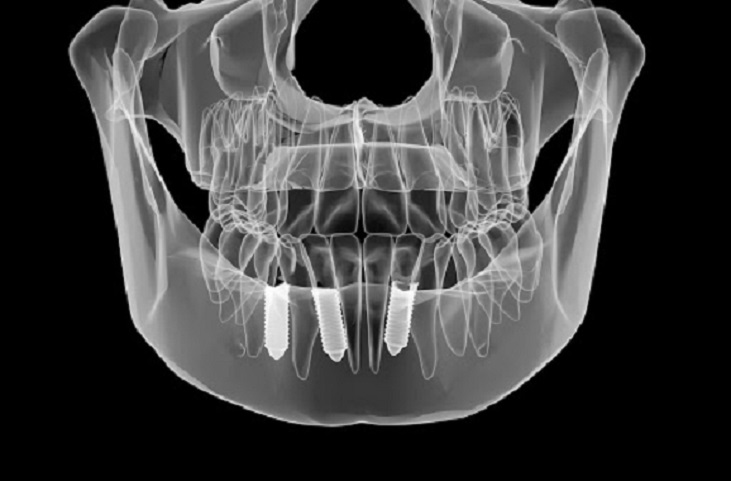
Furthermore, zirconium alloy is biocompatible and can, therefore, be used for implantation in the body. In the medical field, Zr-2.5Nb alloy can be made into knee or hip implants. This zirconium alloy material can reduce friction and increase wear resistance while maintaining overall performance, providing a good solution for medical implants.
Conclusion
Thank you for reading our article, and we hope it can help you have a better understanding of zirconium alloys. If you want to know more about zirconium and zirconium alloy, you can visit Advanced Refractory Metals (ARM) for more information.
Headquartered in Lake Forest, California, USA, ARM is a leading manufacturer & supplier of refractory metals & alloys throughout the world. We provide customers with high-quality refractory metals such as tungsten, molybdenum, tantalum, rhenium, titanium, zirconium, etc. at a very affordable price.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}






