What Is the Industrial Diamond?

What Is the Industrial Diamond?
Tungsten is a metal element with an atomic number of 74 and an atomic weight of 183.84. It’s usually steel gray or silver-white with high hardness and high melting point. It has air corrosion resistance at room temperature. The main application of tungsten is manufacturing filament, high-speed cutting alloy steel, and super-hard mold. Besides, tungsten is also used in optical instruments and chemical equipment. China has the largest tungsten storage in the world.

Tungsten
Among all the refractory metals, tungsten has the highest melting point. As a refractory metal, the biggest advantage of tungsten is its high-temperature strength with good corrosion resistance to molten alkali metal and steam. Tungsten will only have oxide volatilization and liquid phase oxides.
However, the shortage of tungsten is its plastic-brittle transition temperature is too high to be manufactured at room temperature. Refractory metals with tungsten as a representative are widely used in metallurgical, chemical, electronics, light, machinery, and other industries.
Tungsten “Industrial Diamond”
Tungsten belongs to the category of nonferrous metals. The strength and hardness of non-ferrous alloys are generally higher than that of pure metal.
Besides, nonferrous metals have stronger resistance and a smaller temperature coefficient of resistance, which means they have a good combination of mechanical properties.
As one of the nonferrous metals, tungsten has the qualities of high strength and hardness. Therefore, tungsten carbide with high hardness and great wear resistance has a large-scale application in cutting tools and mining tools.
As one of the typical rare earth materials, tungsten is a strategic metal because it is an important part of high-tech new materials. Many electronic optical materials, special alloys, new functional materials, and organometallic compounds need tungsten as essential raw material.
Besides, tungsten is widely used in communication technology, computer science, aerospace development, health care, photographic materials, optoelectronic materials, energy materials, and catalyst materials.

Tungsten Alloy Knife
Industrial Diamond for Military Industry
The armor piercings for tank guns are made from tungsten alloy and depleted uranium alloy. Tungsten is the base for tungsten alloy with other elements added in. With a high melting point, high-temperature strength, good creep resistance, conductivity, and electron emission properties, tungsten is the ideal material for manufacturing hard alloys.
In the 1970s, because of tungsten’s high density, the military industry begins to develop tungsten heart APDS. The warheads use decladding technology and the new structure of the tungsten alloy. The tungsten heart APDS has the characteristics of high initial velocity, low trajectory, short time of the fight, high precision of location, and large penetration, which help hit the fast-moving target effectively.
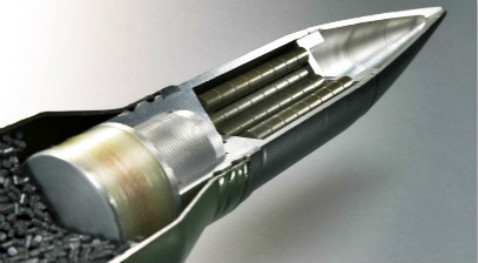
Tungsten Alloy Armor Piercing
The shell heart section of tungsten heart APDS has great density and good scalability. Splashing armors have a double penetration feature which has obvious effects on the armors with big angle, multi-layer structures.
Many Armies have applied tungsten heart APDS in large-caliber bullets and small-caliber shells, which can beat the enemy’s M1, M2 tanks, and other armored vehicles, as well as AH-64 armed helicopters and other light armored targets.
Ban on Depleted Uranium Bombs
Depleted uranium, known as D-38, is actually the nuclear waste after nuclear burning. Its density is 24 times of steel’s. The armor piercings made from depleted uranium can release chemical reactions of 6000°C during exploration.

Depleted Uranium
Depleted uranium not only has radiation but also contains chemical toxicity. Similar to lead and cadmium, uranium is a heavy metal that can cause poisoning. The great heat caused by the exploration of depleted uranium bomb warheads can make the uranium oxide smoke spread to 40 km away. The powder from the uranium exploration can cause radioactive contamination as dangerous as that caused by the exploration of the atomic bomb.
The only difference is that the contaminated area of uranium is a little smaller. However, once these powders enter the human body, their toxic effects will harm human health. The powder will be accumulated in the bone, kidney, and liver, which is likely to cause renal failure and lead to many diseases including cancers, leukemia, and some nervous system disorders. What’s worse, it can lead to miscarriages and abnormal newborns.

D-38 Bomb
Roger Coghill, a British biologist, asked NATO to ban the use of depleted uranium weapons in the European Parliament. Later, the European Parliament adopted a resolution calling on NATO to forbid the use of depleted uranium weapons and to carry out "all necessary measures" to protect human health and the environment. After the ban on uranium bombs, the manufacturing material for armor-piercing is tungsten alloy only. In general, tungsten has great magic as industrial diamond.
conclusion
Thank you for reading our article - What Is the Industrial Diamond? and we hope it can be helpful to you. If you want to know more about tungsten and other refractory metals, you can visit Advanced Refractory Metals for more information. We provide our customers with super high-quality tungsten products and other refractory metals at a very competitive price.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}






