Iridium Uses & Properties
Iridium Uses & Properties
Iridium belongs to the transition element of Group VIII of the periodic table. Iridium is a rare precious metal with the element symbol Ir, atomic number 77, and an atomic weight of 192.2. The content of iridium in the earth's crust is one ten-millionth, and it is often dispersed together with platinum group elements in various ores of alluvial deposits. In this article, let's take a look at the iridium uses & properties.

Iridium Uses & Properties
Iridium Uses
1. The Ues of Iridium in the Industrial Field
The application of iridium mostly uses its high melting point, high hardness, and corrosion resistance. Iridium metal, along with iridium-platinum alloy and osmium-iridium alloy, has a very low loss and can be used to manufacture porous spinnerets. Spinnerets are used to extrude plastic polymers into fibers, such as rayon. Osmium-iridium alloys can also be used for compass bearings and weight scales.
Iridium has strong corrosion resistance and high-temperature resistance, so it is very suitable as an alloy additive. Some long-term components in aircraft engines are made of iridium alloy, and the iridium-titanium alloy is also used as a material for underwater pipes. The addition of iridium increases the hardness of the platinum alloy. Pure platinum has a Vickers hardness of 56 HV, while platinum alloys containing 50 percent iridium can exceed 500 HV.
Iridium is also often used in instruments that must withstand high temperatures. Iridium alloy can resist arc erosion, so it is an ideal material for spark plug electrical contacts. Captiva catalytic method is the process of converting methanol into acetic acid. In this process, iridium compounds can be used as catalysts.
2. The Ues of Iridium in the Medical Field
The radioisotope iridium-192 is an important energy source in γ radiography, which helps in the non-destructive testing of metals. In addition, brachytherapy uses the gamma rays released by Ir to treat cancer. This treatment method places the radiation source near or inside the cancer tissue and can be used to treat prostate cancer, cholangiocarcinoma, and cervical cancer.
3. The Ues of Iridium in the Science Field
Made in 1889, the International Prototype Metre is made of an alloy containing 90 percent platinum and 10 percent iridium and is kept by the international bureau of Weights and Measures near Paris.
Unmanned spacecraft such as Voyager, Viking, Pioneer and Cassini-Huygens, Galileo, and New Horizons have all used thermal motors containing radioactive isotopes of iridium. Since the thermal motor has to withstand high temperatures up to 2000 ° C, the container wrapped with plutonium-238 isotope is made of iridium which is both hard and high-temperature resistant.
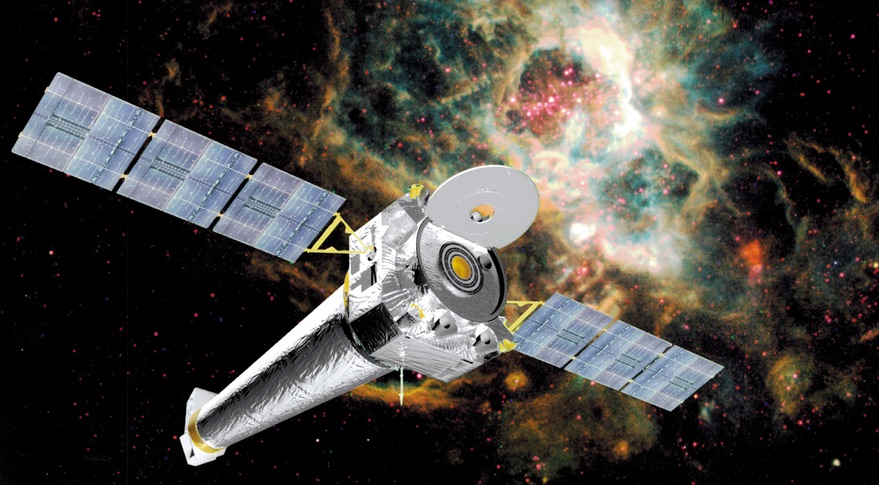

Iridium Uses in X-ray Telescopes
Iridium is also used in X-ray telescopes. The mirror of the Chandra X-ray Observatory has a 60-nm-thick iridium coating. After testing a variety of metals, the X-ray reflectivity of iridium is proved superior to nickel, gold, and platinum.
Iridium Properties
Iridium is white like platinum, with a little yellow. Iridium is hard and brittle, and its melting point is very high, so it is difficult to cast. The manufacturing process therefore generally uses powder metallurgy.
|
Property |
Iridium Properties |
|
Atomic Number |
77 |
|
Atomic Weight |
192.217 u |
|
Density |
22.56 g/cm³ |
|
Melting Point |
2,446°C (4,435°F) |
|
Boiling Point |
4,428°C (8,002°F) |
|
Oxidation States |
-3 to +9 |
|
Corrosion Resistance |
High, stable in most acids |
|
Hardness |
6.5 (Mohs scale) |
|
Elastic Modulus |
528 GPa |
|
Electrical Resistivity |
4.7 μΩ·cm at 20°C |
1. Physical Properties
- Density: Iridium is one of the densest elements, with a density of 22.56 grams per cubic centimeter. This makes it ideal for applications requiring materials that can withstand extreme pressures and environmental conditions.
- Color and Appearance: Ir has a silver-white hue and a reflective surface, similar to platinum, though it tends to be slightly more brittle and challenging to shape.
- Melting and Boiling Points: One of the most remarkable aspects of iridium is its high melting point of 2,446°C (4,435°F) and boiling point of 4,428°C (8,002°F). These values make it highly suited for high-temperature environments, such as in aerospace and industrial applications.
2. Chemical Properties
- Resistance to Corrosion: Ir is among the most corrosion-resistant metals, remaining stable even in harsh acidic and high-temperature conditions. This exceptional stability makes it suitable for components exposed to extreme environments, such as electrodes and spark plugs.
- Oxidation State: Ir has a broad range of oxidation states, from -3 to +9, although the +3 and +4 states are the most common. Its diverse oxidation states enable its use in complex catalytic reactions, particularly in the chemical industry.
- Chemical Inertness: Ir is relatively inert and does not react with most acids, including sulfuric and hydrochloric acid, making it an essential material for high-purity chemical applications and devices requiring longevity and low contamination risks.
3. Mechanical Properties
- Hardness and Brittleness: Despite being durable, Ir is more brittle than metals like platinum or gold. Its hardness, measured on the Mohs scale, is around 6 to 6.5, similar to that of hardened steel. This brittleness can make it challenging to work with in some fabrication processes, although it remains a valuable choice for components needing wear resistance.
- High Elastic Modulus: With an elastic modulus of approximately 528 GPa, iridium exhibits high rigidity, further reinforcing its suitability for high-stress applications where structural integrity is crucial.
Conclusion
Thank you for reading your article, hoping it can let you have a better understanding of iridium's uses & properties. If you want to know more about iridium and other refractory metals, you can visit Advanced Refractory Metals (ARM) for more information.
Headquartered in Lake Forest, California, ARM is a leading manufacturer & supplier of refractory metals throughout the world. We offer our customers high-quality refractory metal products like tungsten, molybdenum, tantalum, rhenium, titanium, zirconium, etc.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}






