EDM Wire Cutting: How It Works and Its Uses

Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) is a highly precise manufacturing process used to cut or shape conductive materials using electrical discharges or sparks. Among the various forms, wire EDM cutting stands out as one of the most accurate methods for cutting intricate and complex shapes. It is particularly useful for materials that are difficult to machine using traditional methods.
What Is EDM Wire Cutting?

EDM wire cutting involves using a thin, electrically charged wire to cut through a conductive material. The wire, typically made of copper, brass, or tungsten, is continuously fed through the material while electrical sparks are discharged between the wire and the workpiece. These sparks cause localized melting and vaporization of the material, resulting in the precise cutting of the part.
Unlike traditional cutting methods that use mechanical force, EDM wire cutting operates without direct contact between the wire and the material. This allows it to create fine, detailed cuts, even in hard metals or complex geometries that would otherwise be challenging to achieve.
Further reading: Why Can Molybdenum Wire Cut Metal?
How Does EDM Wire Cutting Work?
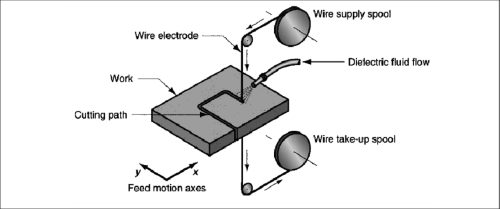 [1]
[1]
- Setup: The workpiece is submerged in a dielectric fluid (often deionized water or oil) that helps dissipate heat and flush away debris during the cutting process. The wire is positioned above the workpiece, and a precise CNC (Computer Numerical Control) system controls its movement.
- Wire Feeding: A thin wire, usually between 0.1 mm to 0.3 mm in diameter, is fed continuously from a spool through the workpiece. The wire is kept taut and guided by two guides, ensuring consistent movement.
- Electrical Discharges: The wire is electrically charged and, when it is brought very close to the workpiece, an electrical discharge occurs. These sparks create temperatures of up to 12,000°C, which are enough to melt and vaporize tiny portions of the workpiece.
- Material Removal: As the wire moves along the programmed path, the continuous series of electrical discharges erodes the material, leaving behind the desired cut. The dielectric fluid flushes away the molten material, preventing the wire from becoming clogged and ensuring a clean, precise cut.
- Finished Cut: After the wire has moved along the designated cutting path, the material is fully separated into the desired shape, with minimal deformation or heat-affected zones.
Advantages of EDM Wire Cutting
 [2]
[2]
- High Precision: One of the biggest advantages of wire EDM is its ability to achieve incredibly precise cuts. Tolerances as tight as 0.001 mm can be achieved, making it ideal for highly detailed and intricate parts.
- No Mechanical Stress: Since the wire doesn’t physically contact the workpiece, there is no mechanical stress or deformation on the material, resulting in clean cuts with smooth edges.
- Ability to Cut Complex Shapes: Wire EDM can cut almost any shape, including internal cuts, contours, and other complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional cutting tools.
- Minimal Heat Affected Zone: Unlike laser or conventional machining, wire EDM produces a smaller heat-affected zone (HAZ), minimizing thermal distortion in the material. This is particularly beneficial for materials that are sensitive to heat or require high precision.
- Ability to Cut Hard Materials: Wire EDM is especially useful for cutting hard materials such as tool steels, titanium, Inconel, and carbide. It is often the only feasible method for cutting these materials.
- No Tool Wear: Since the wire is continuously replaced and is not in direct contact with the material, there is no tool wear, reducing operational costs and increasing the lifespan of the machine.
Uses of EDM Wire Cutting
Wire EDM is used across various industries, particularly where high precision and complex shapes are required.
-
Tool and Die Making
Wire EDM is essential in producing precision dies, molds, punches, and extrusion tools, especially when intricate profiles and tight tolerances are required. Its ability to machine hardened materials directly without distortion makes it ideal for this application. -
Aerospace Components
In the aerospace industry, where performance and safety demand perfection, EDM wire cutting is used to manufacture engine parts, fuel nozzles, and structural components from materials like titanium, Inconel, and hardened stainless steel. -
Medical Devices
Wire EDM is a key technology in the production of surgical tools, implants, and precision components. It delivers the smooth finishes and tight dimensional accuracy needed for medical-grade parts, all while minimizing thermal damage to sensitive materials. -
Automotive Industry
The automotive sector uses EDM wire cutting for gears, transmission parts, and high-precision prototype components. It supports both rapid development and full-scale production of complex shapes in hardened metals. -
Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing
With the need for fine features and complex geometries, EDM wire cutting is ideal for producing connectors, leadframes, and metal enclosures in electronic devices. It offers the precision needed for miniaturization and reliable performance.
Conclusion
Wire EDM cutting is a vital process in modern manufacturing. From aerospace and automotive industries to medical device manufacturing and precision tooling, wire EDM enables the creation of intricate parts and components that are otherwise impossible to achieve with traditional methods.
Molybdenum cutting wire is a vital tool for precision machining, offering excellent strength, heat resistance, and wear resistance. Its ability to maintain performance in demanding environments makes it a preferred choice for industries that require high-precision cuts in tough materials. Advanced Refractory Metals (ARM) is your trusted partner for sourcing high-quality molybdenum cutting wire, ensuring the reliability and efficiency of your manufacturing processes.
Reference:
[1] Bisaria, Himanshu & Shandilya, Pragya. (2015). Machining of Metal Matrix Composites by EDM and its Variants: A Review. 10.2507/daaam.scibook.2015.23.
[2] Ruszaj, Adam & Grzesik, Wit. (2012). Manufacturing of Sculptured Surfaces Using EDM and ECM Processes. 10.1007/978-1-4471-2356-9_7.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}






